AHULife
Under AHULife, the Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate provides a tool for calculating the energy demand and life cycle costs of air handling units. The energy demand is simulated based on hourly resolved weather data and internal loads. The user can choose between various configuration options.
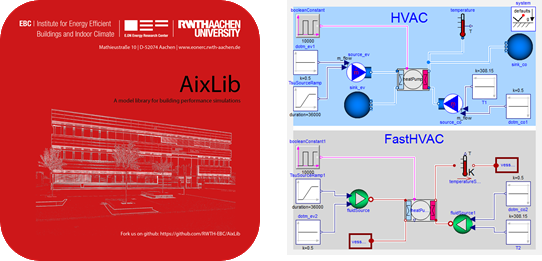
AixLib
AixLib is an open-source Modelica model library for building performance simulations. It contains Modelica models for building envelope and HVAC equipment such as boiler, radiator, heat pump and CHP. Emerging out of the Institute’s needs in research and teaching, AixLib contains models of different level-of-detail. The library extends the collaboratively developed Annex60 library, which focuses on basic model.
CityGML ADE Energy
This extension of the CityGML standard for urban information modeling as an Application Domain Extension (ADE) defines a data model for urban energy analyses, aiming to be a reference exchange data format between different urban modelling tools and databases. It has been developed by an international consortium of urban energy simulation experts.
BUDO Schema
The BUDO Schema (Buildings Unified Data point naming schema for Operation management) structures the designations of data points in the building in such a way that an operator and a machine can interpret them. This structured data can be used for error analysis, optimization or measure development with the help of artificial intelligence within a building energy system.
EHDO
EHDO is a webtool supporting the planning process of complex energy supply systems. The tool has been developed by Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate at RWTH Aachen University for academic teaching. EHDO supports the planning of future energy supply systems and to estimate the potential of renewable energies and future energy carriers like hydrogen. A wide range of innovative technologies like fuel cell, electrolyzer, hydrogen storage, photovoltaic and wind turbines as well as biomass and waste-to-energy technologies can be considered in the tool.
RisiCo
RisiCo is a tool that can be used to determine the relative risk of infection by aerosol-borne viruses in indoor spaces as a function of exclusively technical parameters and characteristics of the persons present for two reference environments. The reference environment corresponds to a mechanically ventilated classroom according to the state of the art, which has a comparatively low absolute risk of infection according to the current state of knowledge.
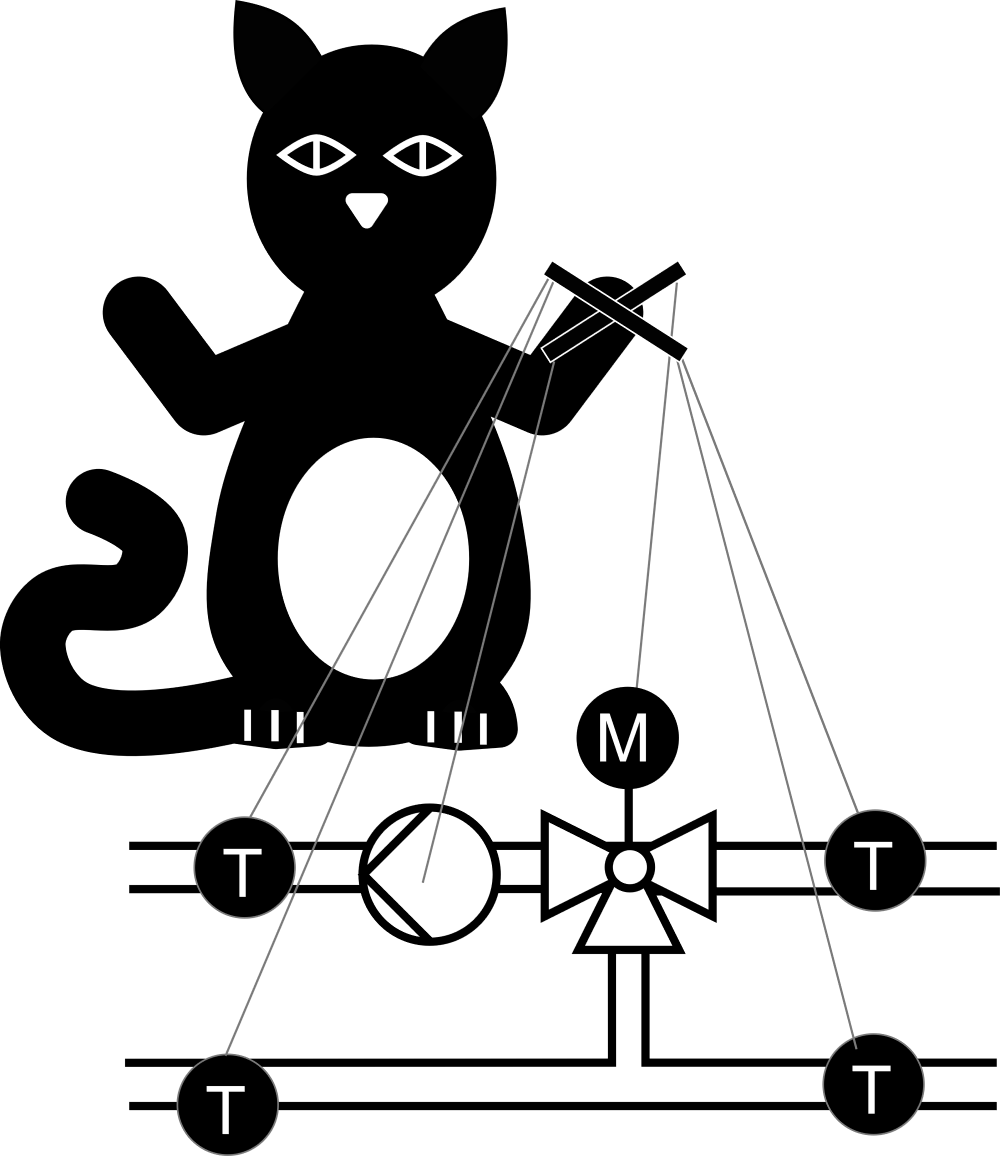
AixOCAT
AixOCAT is an open source software library for the implementation of control algorithms in building automation systems and test benches. This library features support for different software tools that can be used for the implementation of control algorithms as well as support for various commonly used communication/signal transmission interfaces.
BESMod
BESMod is an open-source Modelica model library for the dynamic simulation of domain-coupled simulation of building energy systems. BESMod provides typical modules encompassing the building envelope, hydraulics, controls, ventilation, electrics, user, DHW, and weather using models from various open-source Modelica libraries.
bim2sim
bim2sim is an open source Python library for creating simulation models for various purposes based on BIM models in IFC format. The library provides base code with the ability to map IFC data into a unified metastructure tailored to simulation use cases in the building sector. Additionaly we already provide Plugins for bim2sim for building energy performance simulation and HVAC simulation.
DistrictGenerator
The DistrictGenerator is a tool designed for generating building-specific load profiles and evaluating the energy supply systems of neighborhoods. It has been developed for practitioners such as municipalities, utility companies, and architects, as well as for researchers. The DistrictGenerator thus supports the early planning phases of future neighborhood solutions with renewable energy sources.
Data Trustee Technology Toolbox
A set of technical components supplements existing data trust models (DTM) with concrete technical perspectives. Three core requirements are addressed: interoperability, data minimization, and data security. Technical components are assigned to the respective models and requirements, enabling organizations to plan the technical implementation of their DTM at an early stage.